Blood Constituents
Blood is a red, viscous, liquid connective tissue. It is composed of plasma and formed elements (red blood cells, white blood cells and blood platelets).
Blood is a tissue because it contains specialized cells. More specifically, blood is the only liquid connective tissue in the human body. It is distributed throughout the body by the circulatory system.
Blood is also a colloid. Centrifugation of a blood sample separates its main constituents based on their density. Plasma accounts for about 55% of the blood volume, while the formed elements make up the remaining 45%.
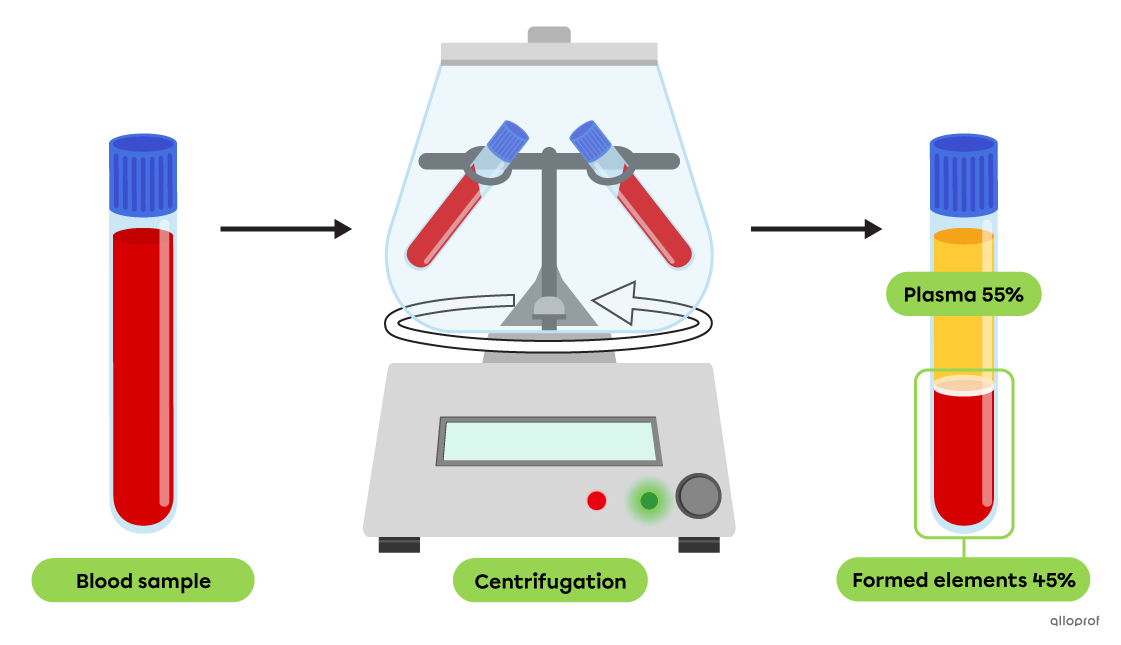
The separation of main blood constituents by centrifugation
Formed Elements
Formed elements, sometimes called cellular elements, are cells and cell fragments found in the blood. They are sometimes referred to as the solid component of the blood.

Blood constituents and their functions (summary)
Plasma
Plasma is a yellow aqueous solution (|\approx90\%| water). It is high in proteins and nutrients. It also contains all the other substances that are transported by blood, such as hormones, antibodies and cellular waste.
Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are immersed in plasma.
Donated plasma
Kzenon, Shutterstock.com
Important!
The main functions of plasma are to contain and transport formed elements, nutrients, hormones, antibodies and waste products throughout the body.
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, are the most abundant cells in the blood. They are soft and have a biconcave disc shape that resembles a doughnut. They have no nucleus and very few organelles. This structure allows them to have a large surface area relative to their size.

Red blood cell
Important!
The main functions of red blood cells are to bind and transport respiratory gases: oxygen |(\text{O}_2)| and carbon dioxide |(\text{CO}_2).|
In order to be transported with the rest of the blood, |\text{O}_2| and some |\text{CO}_2| temporarily bind to the red blood cells. The cell membrane of each red blood cell contains about 250 million[1] hemoglobin molecules.
Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that can bind |\text{O}_2| and |\text{CO}_2.|

Oxygen and carbon dioxide binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells
Blood is red because of the large amount of hemoglobin it contains. In addition, the colour of blood varies depending on the gases that are bound to the hemoglobin. When bound to |\text{O}_2,| hemoglobin becomes bright red. When bound to |\text{CO}_2,| hemoglobin becomes dark red.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are cells that specialize in defending the organism. They have a nucleus, which can be round, kidney bean-shaped or multi-lobed. The shape of the nucleus is the main way to distinguish between the different types of white blood cells.

Different types of white blood cells and their nuclei
Important!
The function of white blood cells is the defence against infections.
White blood cells work to protect the body in several ways. Some are used to detect infections. Others enable the release of antibodies. Finally, some white blood cells are capable of enclosing and eliminating bacteria through the process of phagocytosis.
Platelets
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are cell fragments without a nucleus.

Platelets
Important!
The function of blood platelets is to seal tears in the blood vessel walls to prevent blood loss.
Platelets play an important role in blood clotting (coagulation) and wound healing. When a blood vessel is ruptured, blood platelets are quickly activated. They pile up and collect in the wound to form a temporary plug, which seals the tear.
