The Human Body
On its own, the cell can perform a variety of tasks (digestion, respiration, displacement, reproduction, etc.). However, to perform even more complex tasks, cells can organize themselves and assemble to form multicellular organisms.
Levels of Organization
By assembling together, cells form tissues which, in turn, unite to form organs. Several organs organize to create a system. A set of systems can thus ensure the functioning of any living organism.
These elements, which are called levels of organization, can be placed in increasing order of complexity. These levels of organization range from simpler structures, such as atoms and molecules, to more complex structures, such as the entire organism.
Here are the 7 levels of organization :
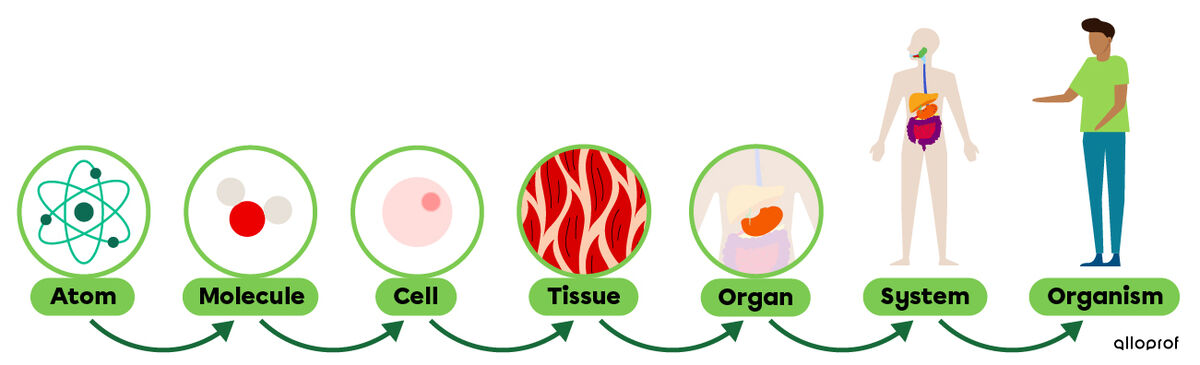
Levels of organization in the human body
Biological Systems
A biological system is a collection of cells, tissues and organs that perform one or more common functions.
The systems of the human body are classified under 3 main functions:
1. The function of nutrition: The need to feed and breathe
2. The function of responsiveness: The need to maintain one's balance and interact with one's environment
3. The function of reproduction: The need to reproduce to ensure the survival of species
